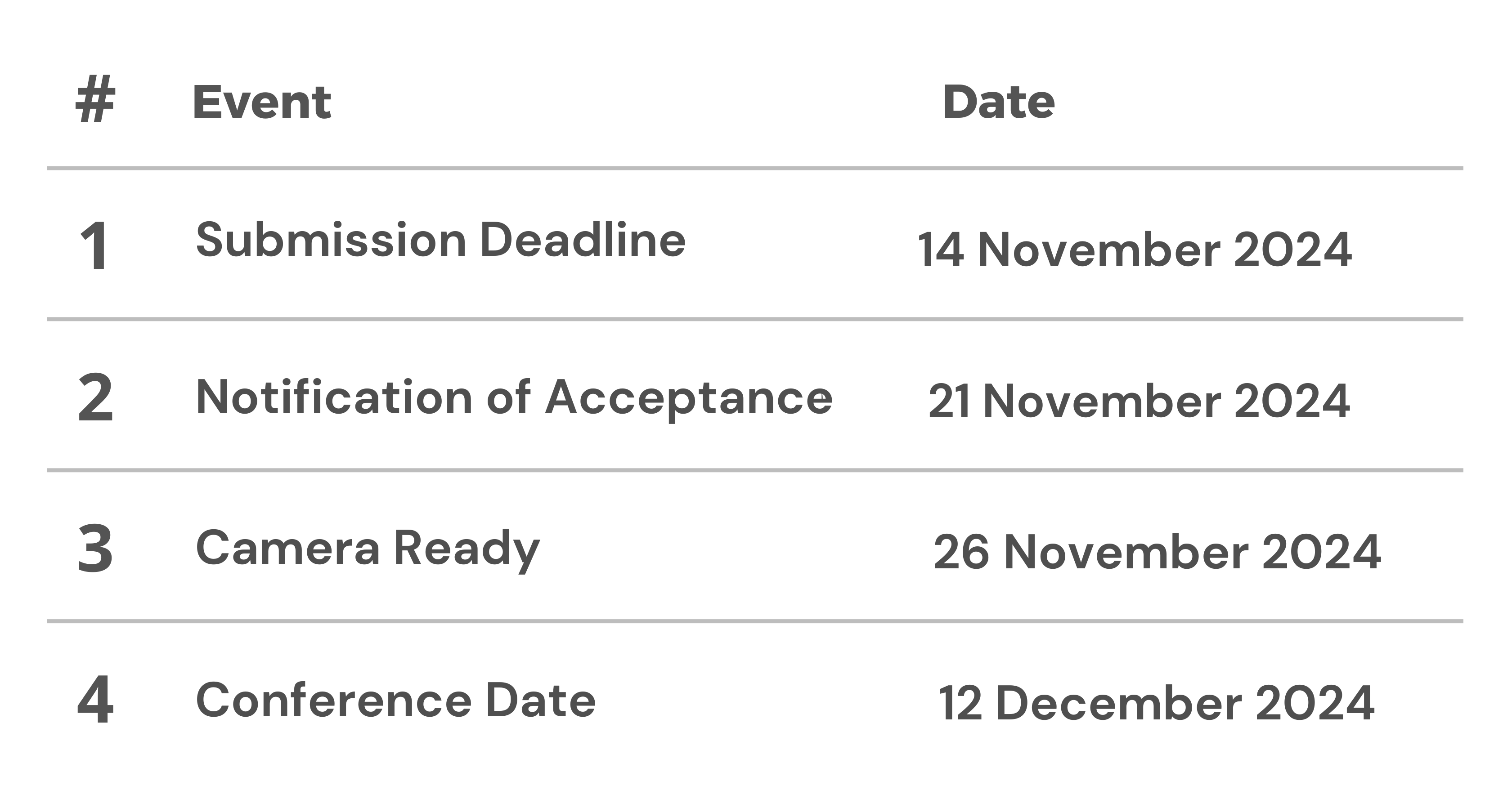
Performance Comparison of Bang-Bang Controller, Single PID Controller, and Cascade PID Controller on Cart Pendulum
Abstract
In midst of new development advance of controller in control theory studies, classical proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controller and it combinations are considered the most applicable and widely used controller. PID controller is a simple yet effective controller to applied in linear systems. It is what makes it used in 95% of control loops process in industries. Although its linearity is what makes it harder to implement when the system becomes more complex, non-linear application of several variable to consider. Other types of control system can handle it with completely different ways using state space model of the system. But a more quick method is by develop a second loop of PID control. This paper focus on performance comparison for stabilize gravitational pendulum on a cart using bang-bang control, single PID Control, and cascade PID control. The system parameters such as rise time, steady time, overshoot and distance traveled will also measured. The result shows the significance of PID control for sistem stablization over simple on/off control or bang-bang control. While conventional single PID controller does the job more efficiently, in real application cascade PID controller shown to be more realistic to consider for system limit and capability.
References
I. Kafetzis and L. Moysis, “Inverted Pendulum: A system with innumerable applications,” Mar. 2017.
H. OUSSAMA, B. MOHAMED, Z. ABDENNOUR, and S. HİCHEM, “Tracking control of a ball on plate system using PID controller and Lead/Lag compensator with a double loop feedback scheme,” European Journal of Science and Technology, Sep. 2021.
C. Zhao and L. Guo, “PID controller design for second order nonlinear uncertain systems,” Science China Information Sciences, vol. 60, no. 2, Feb. 2017.
M. L. Fadhlurrahman, S. Sumaryo, and A. S. Wibowo, “Implementasi Pengendali Ganda PadaTangki Kembar Mengunakan Kendali PI Kaskade,” in e-Proceeding of Engineering, 2018, pp. 3903–3910.
R. R. de Bem, M. F. dos Santos, P. Mercorelli, F. N. Martins, A. F. dos Santos Neto, and J. L. S. de Magalhães Lima, “Cascade PID Controllers Applied on Level and Flow Systems in a SMAR Didactic Plant,” in Proceedings of the 2024 25th International Carpathian Control Conference, ICCC 2024, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2024.
Y. Oyama, “Feedback Control (Lesson by Experiment),” Tokyo, 1996.
A. N. Guzmán, C. A. Lúa, J. A. García-Rodríguez, C. Vidrios-Serrano, and M. A. Meza-Aguilar, “Real-Time Embedded Control of Vehicle Dynamics Using ESP32: A Discrete Nonlinear Approach,” Electronics (Switzerland), vol. 13, no. 19, Oct. 2024.
D. K. Prasetyo, M. Fauziyah, and S. Adhisuwignjo, “Kontrol PID Pada Pengaturan Kecepatan Motor AC Berbasis ESP32,” Kohesi: Jurnal Multidisiplin Saintek, vol. 2, pp. 71–80, 2024.
H. Xue, H. Lv, Y. Xiao, and X. Wang, “Cascade PID Control Systems Based on DNA Strand Displacement With Application in Polarization of Tumor-Associated Macrophages,” IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp. 38563–38577, 2023.